Ground system and Measurement
The ground system consists of optical satellite tracking system and lasers for the spectroscopic measurement. In the RIS measurement, absorption spectra of the atmosphere is measured in the round-trip optical path. Vertical profiles or column contents of atmospheric trace species are derived from the measured spectra.
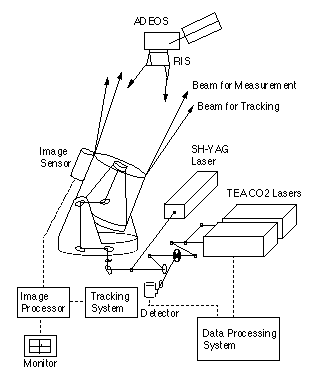
Concept of the RIS experiment
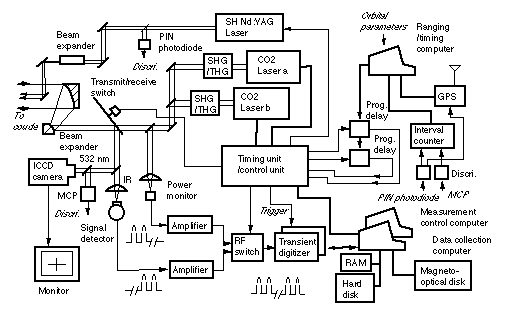
Block diagram of Laser transmitter/receiver system
The tracking telescope with a 1.5-m diameter at CRL is used in the measurement from Koganei, Tokyo. Two single-longitudinal-mode transverse, electric, atmospheric (TEA) CO2 lasers are employed in the spectroscopic measurement. One of the lasers is used for measuring absorption of the target molecule, and the other is used for measuring reference signals to correct atmospheric effects and the angular dependence of reflection of the RIS.
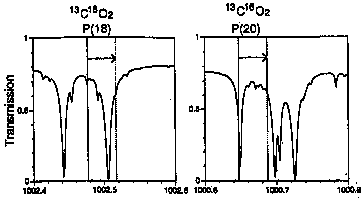
Synthesized atmospheric absorption spectra and the laser lines for the measurement of ozone
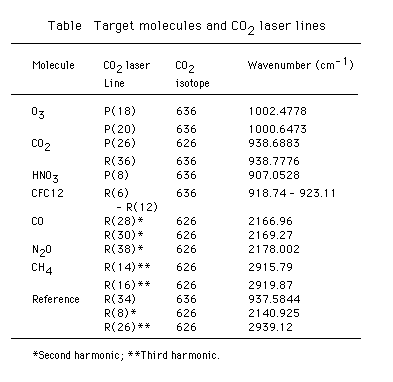
Table lists the target molecules and wave number of CO2 laser lines, which are generated by CO2 lasers with 12C16O2 and 13C16O2 isotopes, and their second and third harmonics. In order to measure the absorption spectrum in wider wavelength regions, the wavelength of one of the laser is switched over several laser lines in a single measurement. Wavelength agile single-longitudinal-mode TEA CO2 lasers were developed for this purpose using the time-gated gain cell method.

RIS on ADEOS
Data reduction and data distribution
return to RIS home page
Detailed information







