Retroreflector in Space (RIS) Experiment
1. Outline of the RIS Experiment
The Retroreflector in Space (RIS) is a large aperture single element cube-corner retroreflector for experiments on earth-satellite-earth laser long-path absorption measurements of atmospheric trace species. The laser long-path absorption method is one of the most sensitive remote sensing techniques for measuring concentration of atmospheric trace species. The RIS experiment was the first implementation of the laser long-path absorption method between the ground and a satellite. The RIS was installed on the Advanced Earth Observation Satellite (ADEOS) which was launched on August 16, 1996.
In the RIS experiments a laser beam was transmitted form a ground station, reflected by RIS, and received back at the ground station. The absorption of the intervening atmosphere was measured in the round-trip optical path. The National Institute for Environmental Studies (NIES) in cooperation with the Communications Research Laboratory (CRL) conducted experiments from a optical satellite tracking facility at CRL in Koganei-City, Tokyo, using a CO2 laser based laser transmitter/receiver system.
Using the RIS, spectrum of atmospheric ozone was measured successfully with the earth-satellite-earth laser long-path absorption method. The operation of the ADEOS was descontinued unfortunately in the end of June 1997 because of the trouble with the solar panel. Because of the discontinuance, we were not able to carry out all the experiments originally planned. Also, we were not able to obtain sufficient data for atmospheric studies. We have obtained, however, valuable data on the measurement technique based on ground-to-satellite laser long-path absorption method.
Studies on accurate orbtal determination of ADEOS was also carried out with the RIS by NASDA, CRL, and Japan Hydrological Department (JHD). 14 laser ranging stations in the world were participated in the RIS tracking support. Orbital prediction approximately 10 times accurate compared with conventional RARR method was achieved with laser ranging. Studies on two color laser ranging were carried out by NASA/GSFC and in Germany.
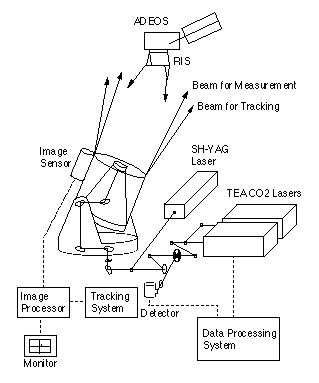
Fig. 1-1 Concept of the RIS experiment.
2. The RIS on the ADEOS
3. Ground system for the RIS experiment
4. Results - Active tracking using image of the RIS
5. Results - Optical characteristics of the RIS
6. Results - Spectrum Measurement with the RIS
7. Results - Orbital Determination of ADEOS by laser ranging to the RIS
8. Future perspective
9. Publications
Return to RIS home page